I am a Linux beginner/amateur and I have sort of had enough of copy and pasting commands I find on the internet without having a good understanding of how they actually work.
I guess my end goal is to be able to comfortably install and use arch Linux with my own customization’s and be able to fix it when things go wrong.
What tips/ideas do you have for getting better at navigating the terminal, and getting a better understanding of how the os works. What is a good roadmap to follow? And how did you, advanced Linux user, get to the stage your at now?
Edit: my current distro is bazzite just in case you were interested and thanks for all the replies you are all really helpful.
Just use it and fix things when they break. There’s no magic bullet - just experience.
start from
man manand learn to use man pages. Get used to lookup man pages for any topic before checking on the internetLearning to read manpages is honestly the best advice. They are pretty dense in information, so maybe that’s why some people go to great lengths to run circles around them looking for inferior sources of information.
This is it. You’re likely not going to get away from needing help from time to time. Instead of focusing on trying to know everything, focus on knowing where to find what you need. It’ll click from there with time.
Linux is like kung-fu, mastery comes through practice
Learn the ways of Linux-fuCommand line cheat sheet (with bonus vim controls):
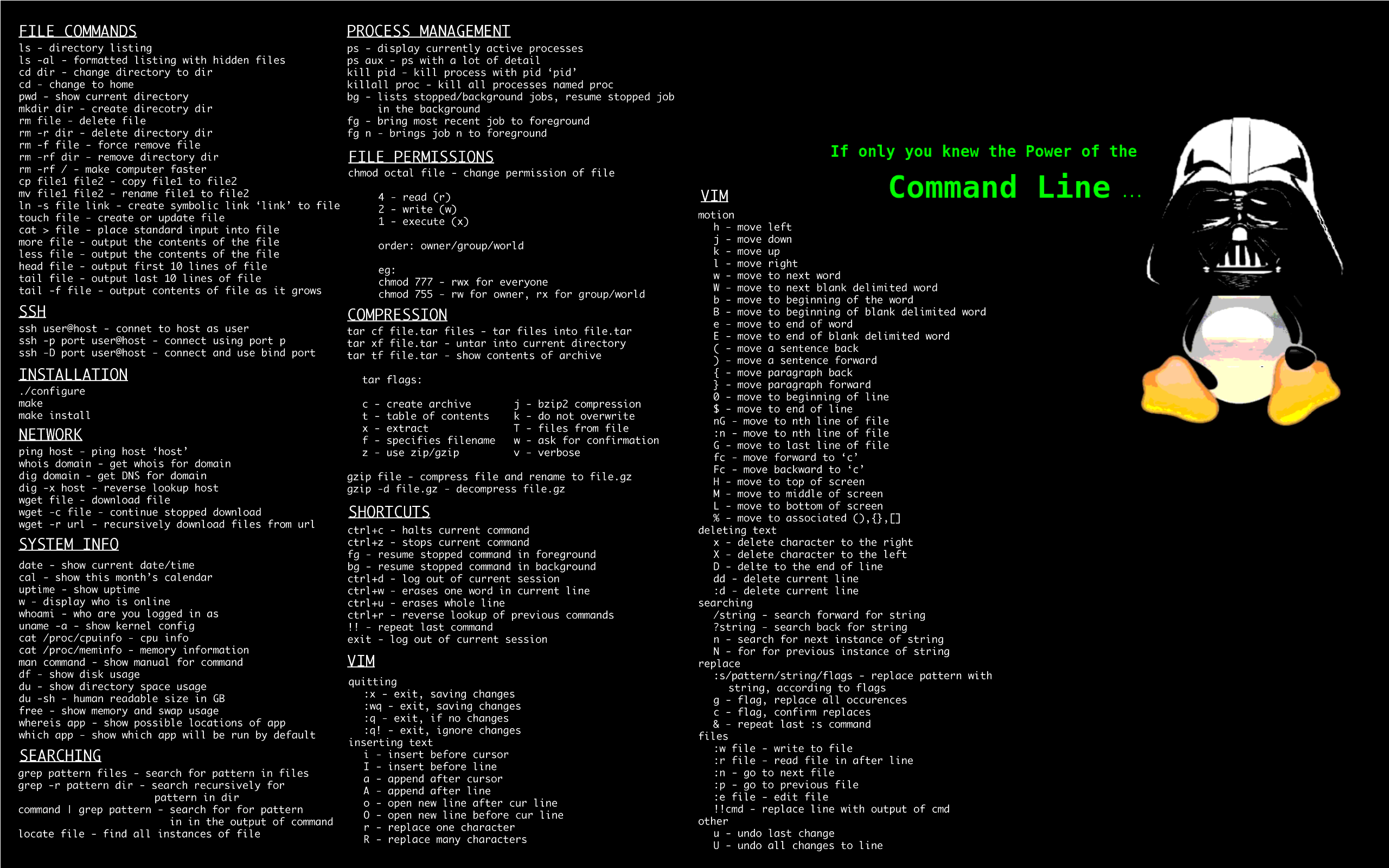
rm -rf /
make computer faster(͠≖ ͜ʖ͠≖)
Wait I did this to my main drive everything went black is this suposed to happen? will it start working again?
That’s kind of awesome, thanks!
And stop copy/pasting them. Type them out so you get used to them. It gets quicker the more you do it.
It sounds a bit nerdy, but dedicate some time just to learning a specific command once in a while. Start with something straightforward like
ls. Read through themanpages and try out all the different options for it. After a while, you’ll master quite a few commands and will be able to string them together to perform more complex tasks. It’s definitely easier learning the system piece by piece like this. I used to learn by just jumping right in to a complex task, but I ended up with just a superficial understanding most of the time. Now days I try to be more deliberate about reading all the documentation and actually learning the tool/command/etc.Also, Arch has the
archinstallscript that greatly simplifies the install process if you need it. You’ll definitely learn more doing it manually though. I’ve been using Arch as my daily driver for a year now and I love it.- To learn Arch, install it from scratch (without archinstall), it’ll force you to read the Wiki and learn a lot of necessary commands in the process. After the installation, just keep using it. Using a Linux distro full-time as the only installed OS is the best way to keep at it and truly learn it over time. There’s no magic bullet here. Just keep using it and solving problems or issues as you go, learning more and more stuff as you go. If you need other OSses as well, run those in a VM. I don’t recommend dual-boot setups.
- Don’t blindly copy/paste commands you don’t understand. Always try to understand them first. Some commands can be very disruptive or even destroy your configuration. If you don’t understand it or are able to adapt it so that it fits to your particular configuration or system, you can EASILY damage a configuration, or even make your system unusable. Also, some people like trolling other people and deliberately share harmful commands. Generally, test potentially destructive commands or complex commandlines before actually running them.
- Document major config changes that you do. This is useful because you’ll be able to undo certain changes or even replicate your current system configuration fast when you change distros or have to reinstall in the future. For example my current Arch-based setup is fully documented in form of an almost-directly executable shell script. It does require some interactions but very little. If I ever have to reinstall this system, or upgrade my hardware, it can be done insanely fast and it’ll have the exact same configuration. This goes from basic partitioning and encryption all the way up to dotfiles and individual program configurations.
- Don’t feel the need to learn hard/advanced tools like Vim or Emacs unless you really think you’re getting an advantage from that and aren’t hesitant to put in the time and effort to learn them. Most people don’t need to use them. They’re amazing tools but you need to be prepared to lose quite a lot of time to learn them before you can become productive with them, and this might not be a tradeoff that’s useful for every single user. You can also get away with much simpler tools, like nano (as a console-based editor) or whatever programmer’s text editor you want.
- Similarly, whether a pure WM or compositor plus assorted tools compared to a full desktop environment is worth it for you or not, is up to you. There’s no wrong or right answer here. I’ve tried out pretty much everything and these days use KDE Plasma because I like the consistency and integrations and dislike having different, inconsistent stand-alone tools for panels, menus, notifications, wallpaper, file manager and so on. But again, there’s no wrong or right answer here. Just what makes more sense for you. It’s worth learning how to be able to configure and use a minimalistic setup, for sure. So trying it out doesn’t hurt and increases your knowledge overall. In general, in the Linux world it’s good to always know enough to not be screwed once some component suddenly doesn’t work anymore. For example, a competent Linux user should be able to deal with (temporarily) not having a GUI and fixing his system via commandline.
- A minimalistic, DIY distro like Arch can be amazing to learn everything, if you want to do that at least. If you just want a working desktop system with as little effort as possible, then don’t do that. But if you intend to learn every detail, then a distro like Arch is better suited for that goal than a “bloated”, fully pre-configured distro like Mint or Ubuntu is. Because Arch is much simpler on a technical level than those are. It’s much easier to understand e.g. the relatively simple package building process on Arch than it is on Debian/Ubuntu-based distros. But this “simple” explicitly refers to technical simplicity or minimalism. Most users expect something else when they hear “something is simple”. Arch is not simple as in beginner-friendly, but it is simple in terms of technical complexity, which is why many advanced users and tinkerers like it because it doesn’t stand in their way. It also means though that you HAVE to learn many things, e.g. how to configure a firewall, because it doesn’t come with any preinstalled by default. With Arch, the admin is supposed to know about everything and configure every component himself, at least on a somewhat basic level.
- If you want to go to even more details, you could also try out a source-based distro like Gentoo or Crux, which can also be a great learning experience, but it’s even more details regarding compilations of each package, dependencies, compile-time options, etc. you have to deal with than with a minimalistic binary-package-based distro like Arch, so whether that’s useful for you or not is up to you of course.
- While we’re at it: LFS (Linux from Scratch) is not a distro per se, it’s a guide on how to build your own distribution from scratch. It’s VERY time intensive and not recommended unless you truly want to learn how to build a complete distribution from scratch, or maybe start your own distro some day which isn’t based on another existing distro.
documented in form of an almost-directly executable shell script
I’m annoyed with myself for not thinking of doing this
Another book rec: https://pragprog.com/titles/bhcldev/small-sharp-software-tools/
deleted by creator
duck duck it
I use searx. Ok but seriously very helpful I will look into that.
deleted by creator
-
Learn FreeBSD.
-
Learn Linux.
/s
-
This course by the Linux Foundation goes over the basics and I thought it was pretty good. I was a long time user of Linux when I came across this and wanted to see how much I really knew. It’s very easy to follow and well structured
https://training.linuxfoundation.org/training/introduction-to-linux/
Using
tldrto learn commands. It gives you the information you are probably looking for in the man page but it’s not buried among lines and lines and lines of arcane stuff and it’s formatted in a readable way with helpful examples. Saved my sanity more than once.I’m not saying “don’t read the man pages”, they are great way to get a deeper understanding of commands. But when you are just wondering what a command does and how it’s commonly used, then a two lines summary + example is much more helpful than an essay going in minute details over everything.
Since it takes a lot less time than hunting the same info in the man page, you can run it before every command you are not familiar with, without too much hassle. Then if you want more info you can check the man page.
If you’re not already, use it as your main system. Don’t dual boot. Stop using windows and mac. When you run into something you need to do, figure out how to do it on linux. It will be slow going at first, but after a few months you will pick up more productivity than you had before.
Another commenter recommended the fish shell, but I disagree because fish is not posix compliant. Almost all of the shell script examples that you will find assume posix compatibility and will usually have to be modified to run with fish. Once you get comfortable with a posix-compliant shell, then maybe consider fish or another “modern” shell.
On the topic of shells, read the bash manual. It’s long and informative. You don’t have to memorize it, but be aware of the different concepts there, and refer to it when you need to. It’s pretty horrible as a programming language, but it’s what glues most of Linux together.
I am still dual booting because some games I play just don’t work properly but other than that I am doing everything I can on Linux.
To be honest, this is my recommendation as well. If you kill Windows and can’t play your favorite games, then its more likely to give up Linux.
erasure edit: ok nvm, thanks
Switch to rolling distro, it will break so many things with each update you’ll learn stuff by fixing it. Also you can check https://overthewire.org/wargames/bandit/
I thought rolling releases were still pretty stable to things really break that often?




